Research Articles
Next-Generation Sequencing in Precision Oncology: A Comprehensive Review of Technologies, Clinical Applications, and Future Directions
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has fundamentally transformed precision oncology by enabling comprehensive genomic profiling of tumors, thus guiding diagnosis, prognostication, and personalized treatment selection.
Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Oncology: From Diagnostic Revolution to Therapeutic Precision
Comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP) represents a paradigm shift in cancer diagnostics, moving beyond single-gene testing to simultaneously analyze hundreds of cancer-related genes and genomic signatures.
DNA Sequence Representation Methods: A Comparative Analysis for Biomedical Research and Clinical Applications
This article provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of DNA sequence representation methods, tracing their evolution from foundational computational techniques to advanced AI-driven models.
Filter vs. Wrapper Feature Selection: A Comparative Guide for Biomedical Data Analysis
This article provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of filter and wrapper feature selection methods, tailored for researchers and professionals in drug development and biomedical sciences.
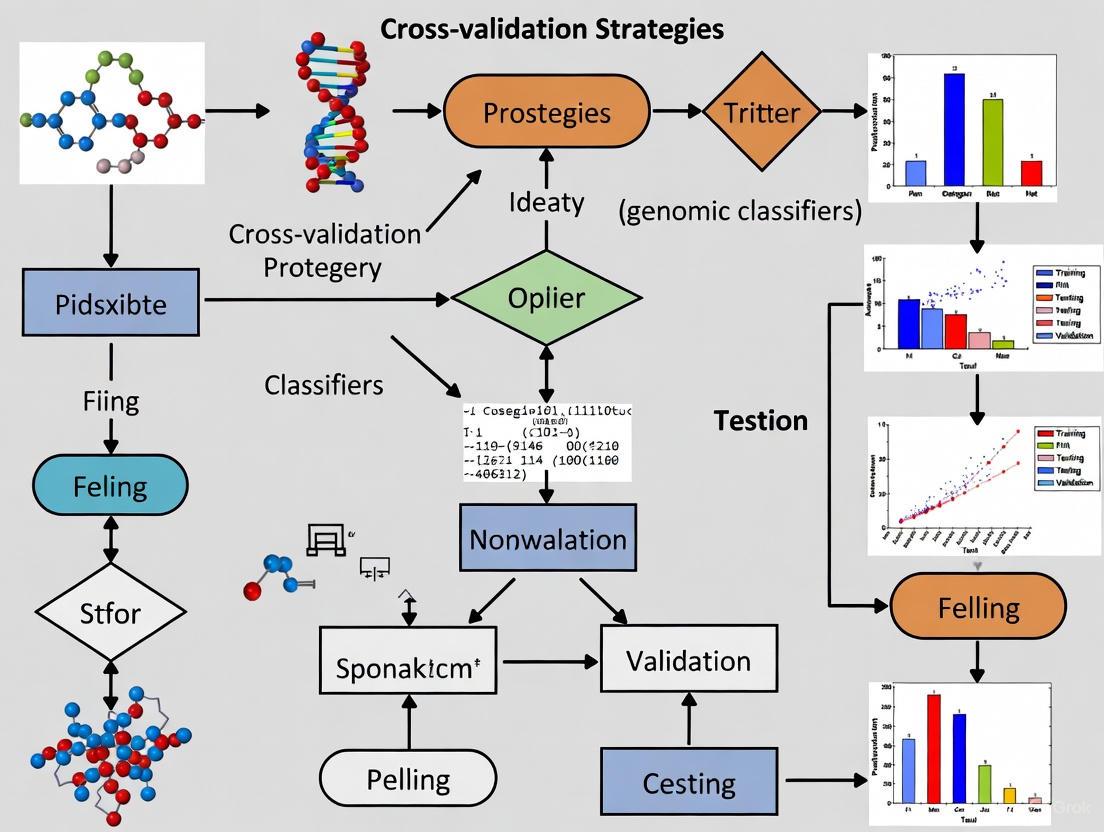
Cross-Validation Strategies for Genomic Cancer Classifiers: A Guide for Robust Model Development
This article provides a comprehensive guide to cross-validation (CV) strategies for developing and validating machine learning models in genomic cancer classification.
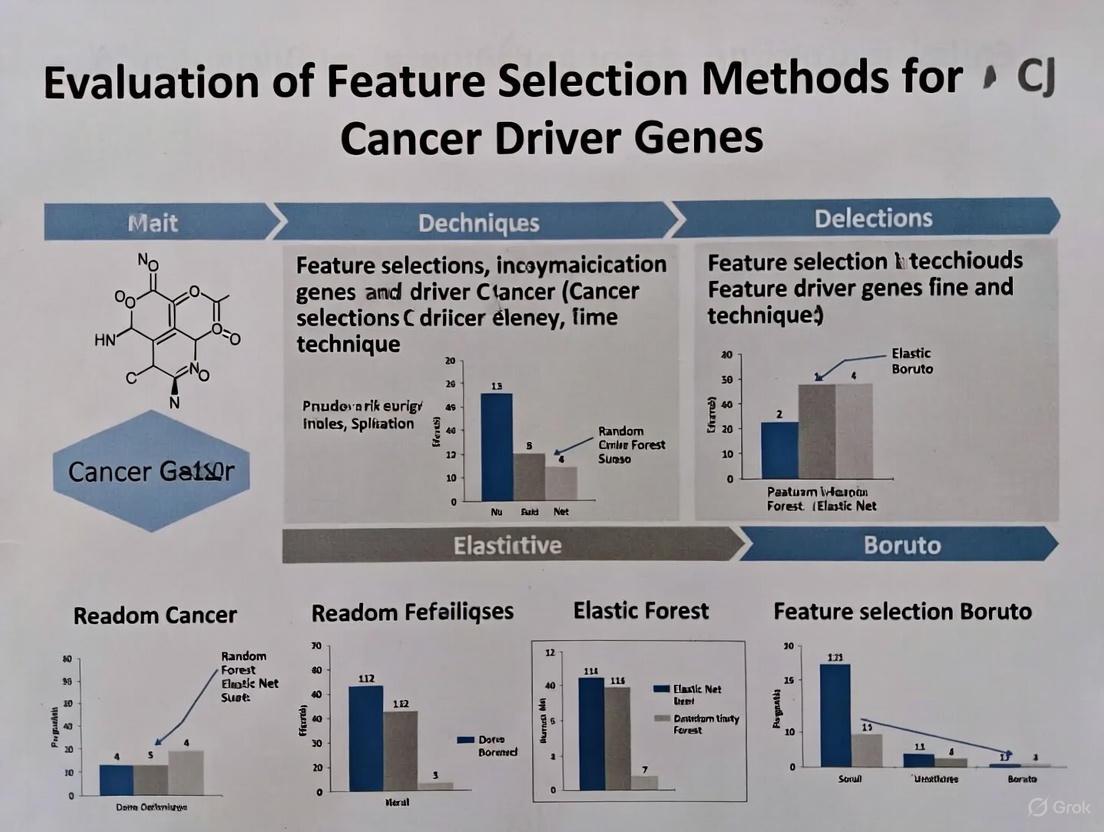
Optimizing Cancer Driver Gene Discovery: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Feature Selection Methods for Precision Oncology
The identification of cancer driver genes is fundamental to understanding oncogenesis and developing targeted therapies.
From Data to Diagnosis: A Roadmap for Clinically Validating cfDNA Machine Learning Models
The integration of machine learning (ML) with cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis holds transformative potential for non-invasive cancer detection, therapy selection, and monitoring.
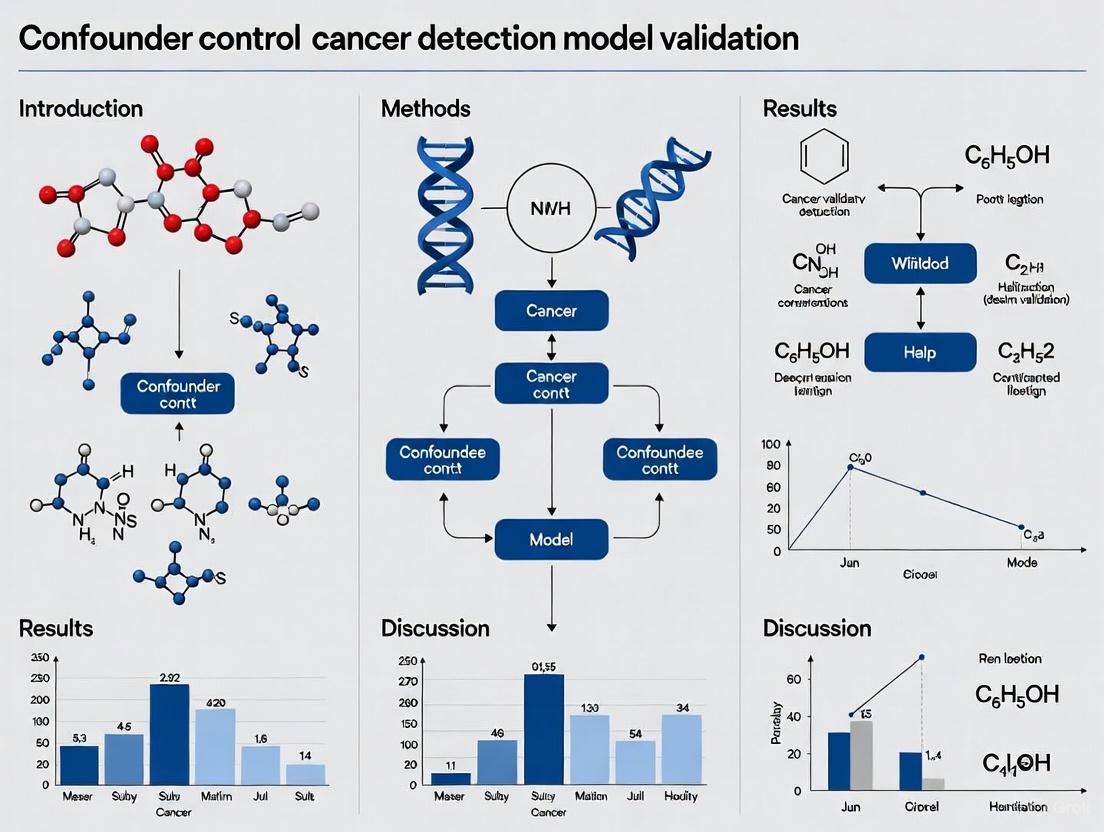
Controlling Confounders in Cancer Detection Models: A Comprehensive Guide to Robust Validation and Clinical Translation
This article provides a comprehensive framework for researchers, scientists, and drug development professionals on managing confounding factors during the validation of cancer detection models.
Beyond the Data Desert: Innovative Strategies to Overcome Scarcity in Medical Genomics Research
This article addresses the critical challenge of data scarcity in medical genomics, a major bottleneck hindering drug discovery and precision medicine.
Overcoming the Low ctDNA Fraction Barrier: Advanced Strategies for Early Cancer Detection and MRD Monitoring
The analysis of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has transformative potential for early cancer detection and minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring.